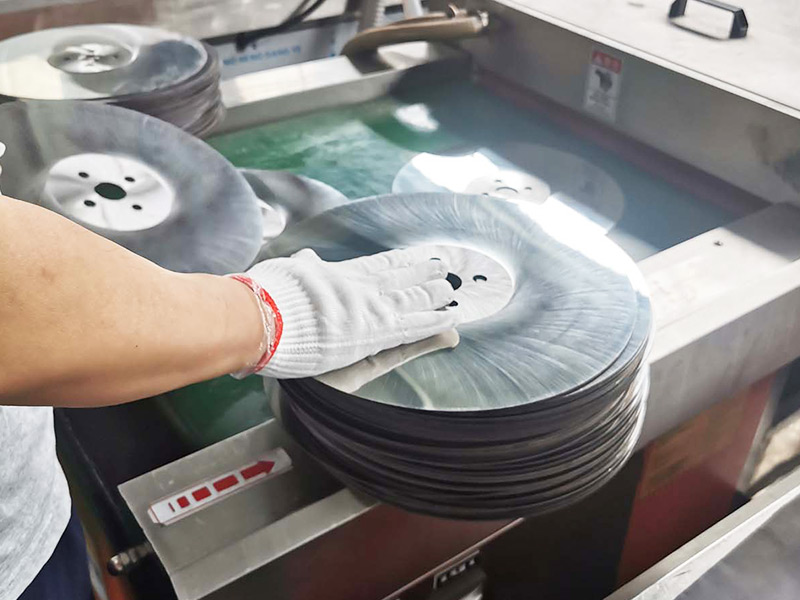
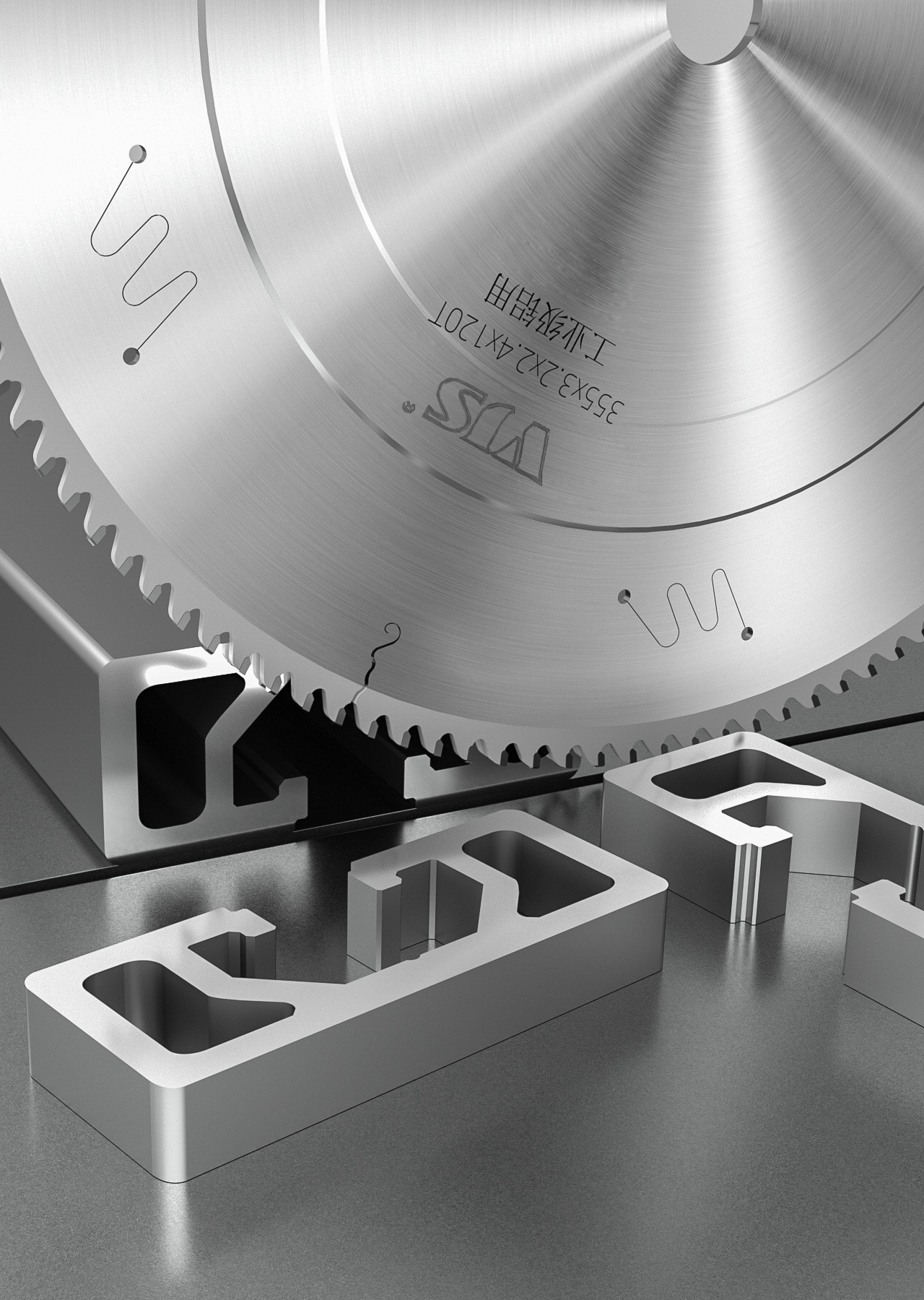
In the field of metal processing, circular saw blades are core cutting tools, and their performance directly affects production efficiency and processing accuracy. Circular saw blades are circular thin-sheet tools with sharp teeth on the edge. They separate metal materials through the cutting force generated by high-speed rotation. It is mainly composed of a saw blade base and saw teeth. The base provides strength and rigidity for the saw blade to ensure stability during high-speed rotation; the saw teeth are the key part of cutting. Their material, shape and arrangement determine the cutting performance and application range of the circular saw blade.
According to the saw tooth material and structural design, metal cutting circular saw blades can be divided into many types, each with unique application scenarios:
1. Alloy saw blade (TCT)
Alloy saw blade, referred to as TCT (Tungsten Carbide Tipped) in English, is a saw blade with cemented carbide fixed to the edge of the base through welding or inlaying. Its main components, tungsten carbide (WC) and binder cobalt (Co), are sintered at high temperature and high pressure to give the saw blade extremely high hardness (HRA89 - 93) and excellent wear resistance, and can withstand high-temperature cutting environments of 800 - 1000℃.
In terms of structural design, TCT saw blades have various tooth shapes. The staggered tooth design can increase the contact area between the cutting edge and the metal, speed up the chip removal speed, and is suitable for fast cutting of ordinary steel; the wavy tooth optimizes the cutting path, reduces cutting vibration, and has a higher cutting surface finish, and is often used in the processing of materials such as stainless steel and aluminum alloys. Precision grinding and edge strengthening treatment further improve the sharpness and durability of the saw teeth.
TCT saw blades are widely used. In automobile manufacturing, it is used to cut high-strength steel for car bodies at a cutting speed of 30-50 meters per minute, and the cutting surface roughness Ra value is controlled at 6.3-12.5μm, which greatly reduces the subsequent grinding process; in the metal door and window processing industry, it can accurately cut stainless steel plates within 5mm, with smooth cutting edges and no burrs, significantly improving production efficiency and product quality.
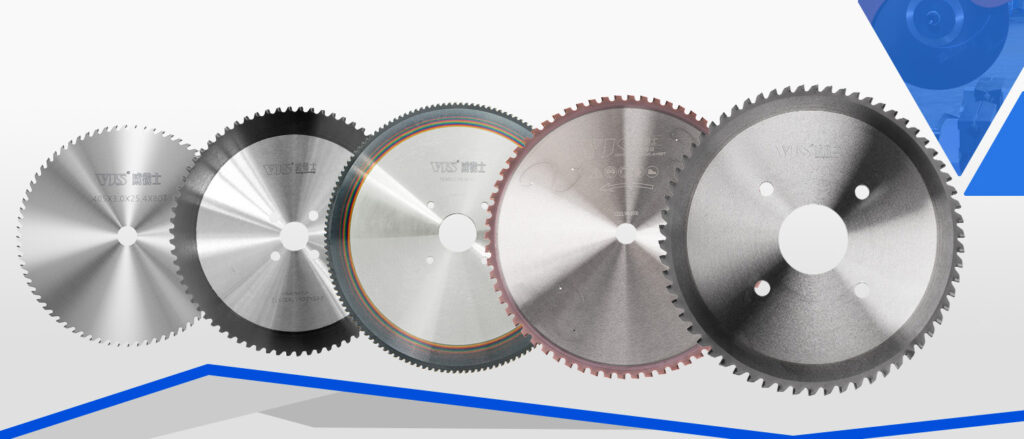

2. High-speed steel saw blade (HSS)
High-speed steel saw blade, referred to as HSS (High-Speed Steel), is composed of various alloy elements such as tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo), chromium (Cr), vanadium (V), etc. After special heat treatment, the hardness can reach HRC62-65. It can still maintain good cutting performance at a high temperature of 600℃, and has both high toughness and red hardness.
This type of saw blade mostly adopts a fine-tooth and dense-tooth design, which has a stable cutting process, strong impact resistance, and can effectively reduce the phenomenon of tooth collapse. For the processing of metal parts with complex shapes and high precision requirements, high-speed steel circular saw blades have obvious advantages. In the field of precision machinery manufacturing, it is often used to cut small shafts and gear parts. For example, in the manufacture of clock and watch movements, metal bars with a diameter of less than 5mm can be cut into precise sizes with a length error of less than ±0.05mm; when manufacturing medical devices, it can also ensure the integrity and stability of the initial cutting of titanium alloy surgical instruments.
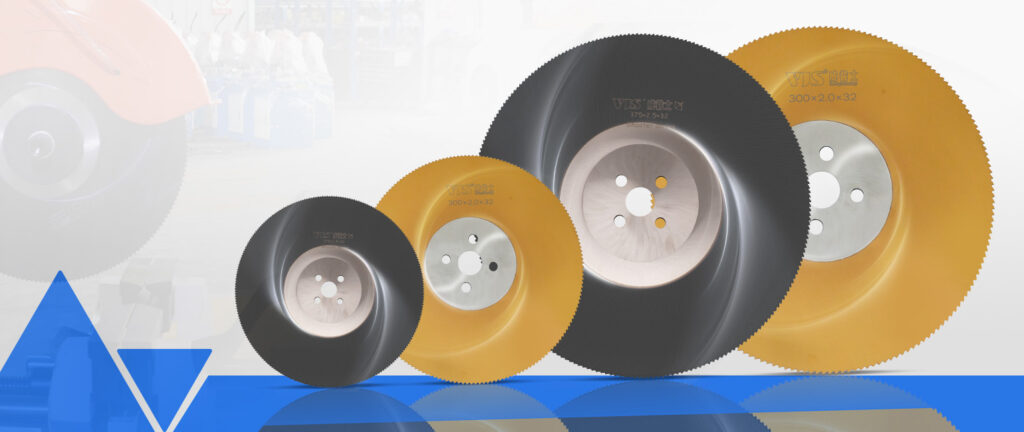

3. Tungsten Carbide Saw Blade (TCS)
Tungsten carbide saw blades are essentially carbide saw blades. The main component of tungsten carbide (WC) is higher, generally accounting for more than 90%, and only contains a small amount of binder. Therefore, the hardness (HRA90 or above) and wear resistance are far superior to ordinary carbide saw blades, and they are especially suitable for cutting extremely hard metal materials.
Due to the relatively large brittleness of tungsten carbide, the design of tungsten carbide saw blades pays more attention to the bonding strength between the matrix and the saw teeth, and often uses thickened matrix or special welding process to enhance the overall toughness. In the field of aerospace, it is used to cut difficult-to-process materials such as titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys, and can achieve a stable cutting speed of 10-20 meters per minute, and the cutting surface accuracy can meet the strict standards of aviation parts; in the mold manufacturing industry, for the cutting and processing of hardened steel molds, tungsten carbide saw blades can efficiently complete the task with their ultra-high hardness and extend the service life of the saw blades.
The metal processing industry's pursuit of cutting efficiency and precision is endless. Carbide saw blades (TCT), high-speed steel saw blades (HSS), and tungsten steel saw blades (TCS) have their own performance advantages and jointly built a diversified solution for metal cutting. With the continuous innovation of material science and manufacturing technology, these saw blades will develop in a smarter and more efficient direction in the future, injecting new impetus into the metal processing industry.