Vacuum Coating for HSS Saw Blades
Install the dried HSS saw blades on the workpiece holder. Ensure proper spacing between the blades, then close the vacuum chamber and start the vacuum pump to evacuate the chamber to a high vacuum level of 10⁻³ - 10⁻⁵ Pa. Introduce inert gas such as argon, and use the ion beam generated by glow discharge to bombard the surface of the saw blades, cleaning and activating the surface. Select appropriate target materials such as titanium nitride (TiN) according to requirements. Through magnetron sputtering or arc ion plating techniques, control the temperature, time, and gas flow rate to deposit the target material atoms or ions onto the surface of the saw blades to form a coating with specific properties. After the coating process is completed, wait for the temperature inside the vacuum chamber to drop to room temperature. Slowly introduce inert gas to restore the pressure, and then remove the saw blades to complete the process.
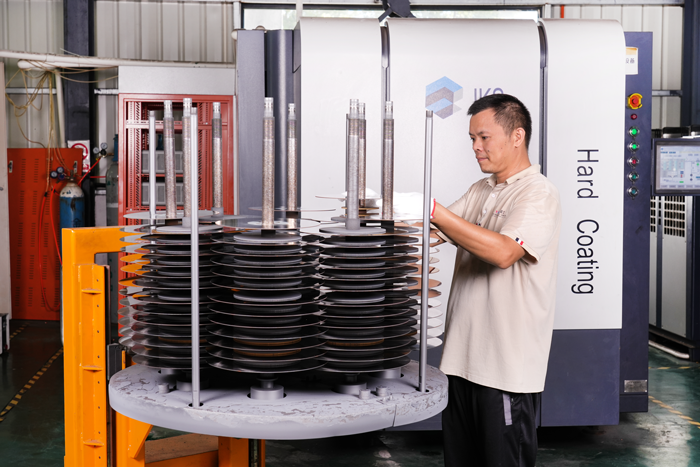
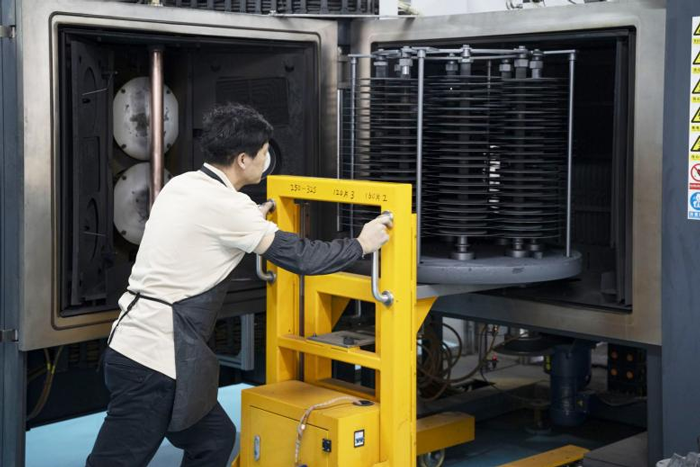
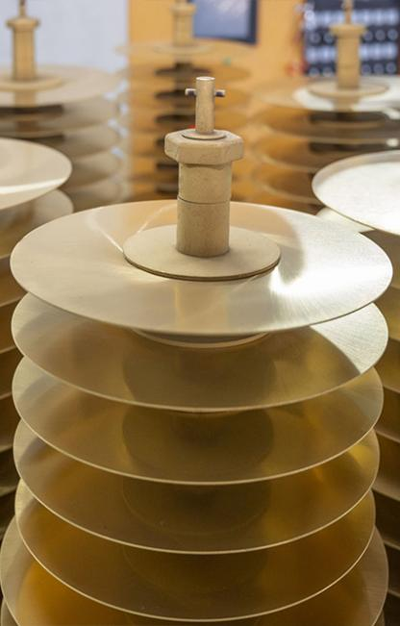
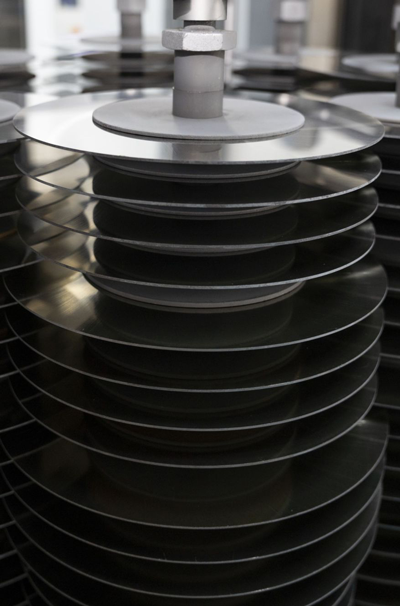




Vacuum Coating for TCT Saw Blades
Similar to HSS saw blades, the cleaned TCT saw blades are gently loaded onto the workpiece rack. After closing the vacuum chamber, the system is evacuated while strictly controlling the clamping force to prevent damage to the carbide tips. First, low-energy ion bombardment is used to remove impurities, followed by differential activation of the tips and substrate through parameter adjustment. A multi-layer composite coating process is employed: a transition layer is applied to the substrate to enhance adhesion, while a wear-resistant layer is coated on the tips and an anti-fatigue layer on the substrate. During coating, the temperature of the tips is monitored to ensure the quality of the welding joints. After coating, the blades are slowly cooled before removal. They must pass visual inspection, thickness measurement, and adhesion testing before proceeding to the next production stage.